Role of the Radiative Effect of Black Carbon in Simulated PM2.5
Concentrations during a Haze Event in China
Role of the Radiative Effect of Black Carbon in Simulated PM2.5 Concentrations during a Haze Event in China |
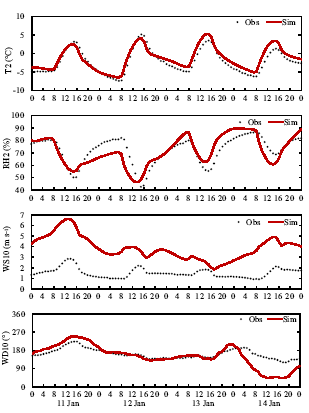
| Figure 1 Simulated hourly variations of temperature at 2 m T2, relative humidity at 2 m RH2, wind speed at 10 m WS10, and wind direction at 10 m WD10 averaged over the heavily polluted region of 31.6-41.0#cod#x000b0;N, 112.0-119.4#cod#x000b0;E during the haze episode of 11-14 January 2013. |
 |