Role of the Radiative Effect of Black Carbon in Simulated PM2.5
Concentrations during a Haze Event in China
Role of the Radiative Effect of Black Carbon in Simulated PM2.5 Concentrations during a Haze Event in China |
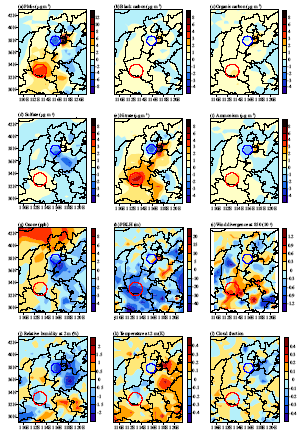
| Figure 3 Simulated differences in concentrations of a PM 2.5 , b BC, c OC, d sulfate, e nitrate, f ammonium, g ozone, and also meteorological parameters of h PBLH, i wind divergence at 850 hPa, j RH2, k T2, and l cloud fraction between 4BC and the CTRL simulations 4BC minus CTRL. Units are indicated at the top of each panel. Simulated differences in concentrations of BC were calculated as a quarter of BC concentration in 4BC minus BC concentration in CTRL. |
 |