As the largest climate signal on the interannual time scale, El Ni?o has pronounced impacts on typhoon activity. Recently, a growing number of studies have been focusing on the climatic effects of the pace of El Ni?o decay and the remarkable role this plays in the genesis position and intensity variations of typhoons. However, the response of the frequency of typhoon occurrence to the pace of El Ni?o decay remains unclear.
In a paper recently published in Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, Dr Qun Zhou and Dr Lixin Wei from the National Marine Environmental Forecasting Center, attempt to address this issue. They present new evidence for variation in the pace of El Ni?o decay having a significant influence on the typhoon frequency in the summer following the mature winter of El Ni?o.
“Firstly, we classified El Ni?o cases into two categories: fast decaying [FD] and slow decaying [SD]. Interestingly, the typhoon occurrence frequency decreased sharply in the following summer only for FD El Ni?o cases. In order to explore the possible reason for this observed typhoon response, we further compared the environmental factors for typhoon development and the related atmospheric circulation processes between the FD and SD El Ni?o years,” explains Dr Zhou.
Compared with those for SD El Ni?o years, fewer typhoons occurred in the following summer for FD El Ni?o years, and the causal mechanism was a stronger anticyclonic anomaly over the western North Pacific forced by tropical Indo-Pacific sea surface temperature (SST) anomalies. Therefore, the pace of El Ni?o decay might serve as an important factor in the prediction of typhoon activity.
“However, the question of how these distinct patterns of tropical SST anomalies establish under FD and SD El Ni?o conditions needs to be studied in future work from the perspective of ocean dynamics,” adds Dr Zhou.
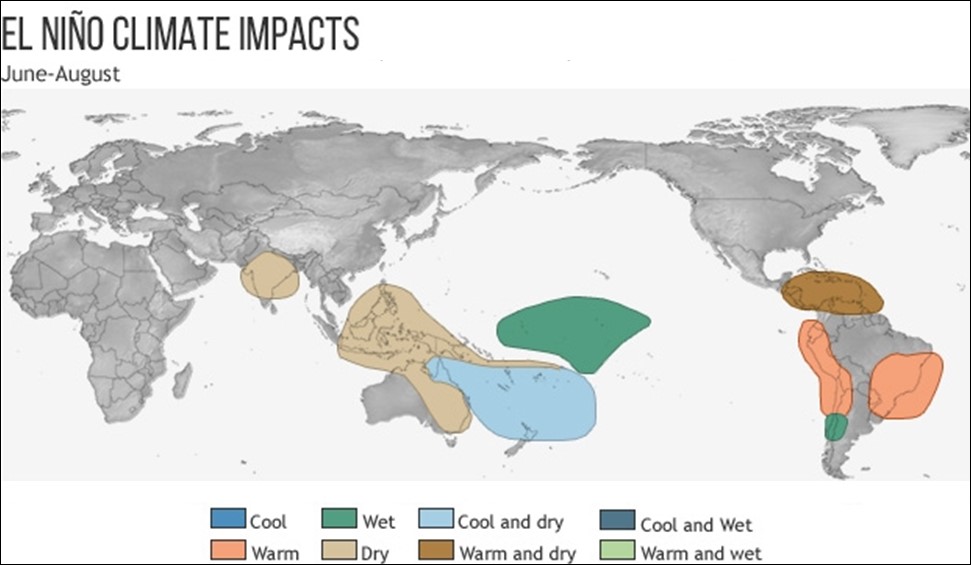
Impacts of El Ni?o events on the global climate in summer (June–August). Source: World Meteorological Organization.
Citation: Qun Zhou, Lixin Wei, 2023, Influence of the pace of El Ni?o decay on tropical cyclone frequency over the western north pacific during decaying El Ni?o summers, Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 100328, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aosl.2023.100328.
Link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aosl.2023.100328
|